carpal compression test sensitivity and specificity|cts sensory test accuracy : distributors Previous studies revealed differences in sensitivity and specificity with values of . Sem dúvidas é a melhor academia de Piraquara, acredito que possa ser melhorada, principalmente em uma modernização dos aparelhos, mas hoje você encontra aparelhos para fazer praticamente todos os treinos mais comuns, fica uma sugestão que não envolve custo, para uma melhor organização da disposição dos pesos, marcação de quanto tem .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Sou femboy, tenho 21 anos e uma mente pervertida. Desde meus 16 anos que minha mente foi “corrompida”, graças à minha curiosidade e a internet. Sempre fui uma pessoa .
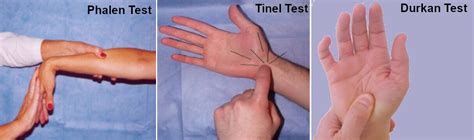
The median nerve compression with wrist flexion (Phdurkan) test was previously described by Tetro et al 6 and was found to have a sensitivity of 0.82 and a specificity of 0.99 for CTS. We found for Phdurkan test a sensitivity of 0.84 and a specificity of 0.11 for the diagnosis .The present study evaluated the sensitivity, specificity and predictive values of six .Our purpose was to assess the diagnostic validity (sensitivity (Sn) and specificity .Previous studies revealed differences in sensitivity and specificity with values of .
The study shows sensitivity and specificity of the Carpal compression test were higher than both Tinel's and Phalen's tests. Also study suggest both CCT and TT were positive, the diagnosis is more likely to be CTS [3]. See the test .The present study evaluated the sensitivity, specificity and predictive values of six clinical tests in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). METHODS: There were 29 carpal tunnel .
A recent meta-analysis of more than 20 studies found a pooled sensitivity of 57% (95% CI, 44% to 68%) and specificity of 67% (95% CI, 52% to 79%) for the Phalen test and a pooled sensitivity of.Carpal Compression Test (Durkan’s) Sensitivity: 64% [6] Specificity: 83% [6] The Carpal Compression Test or Durkan’s Test is performed by holding the patients wrist in slight flexion .
vochtmeter voor muren kopen
Our purpose was to assess the diagnostic validity (sensitivity (Sn) and specificity (Sp)) of physical examination maneuvers for carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). This meta-analysis utilized .This is known as the flick sign, and is 93% sensitive and 96% specific for CTS.6 Other provoking factors include tasks that require repetitive wrist flexion or hand elevation, such as. The manual carpal compression, or Durkan test is performed by applying pressure over the transverse carpal ligament for 30 seconds . Pain or paresthesia indicates a positive .Previous studies revealed differences in sensitivity and specificity with values of 61-91 percent and 33-93 percent for the PT, and 41-74 percent and 80-91 percent for the TT, respectively. 3 .
This study found that the instrumented carpal-compression test had an 89% sensitivity and a 96% specificity in diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome. The instrumented device described in this study is lightweight and simple to use, and provides a rapid and inexpensive method of screening for carpal tunnel syndrome.Sensitivity, specificity and predictive values of carpal tunnel syndrome provocative tests Sensitivity Specificity Positive predictive value Negative predictive value Tinel’s sign 62% 93% 88% 76% Phalen’s test (60 s) 85% 90% 87% 89% Wrist flexion with fingers flexed (60 s) 74% 92% 87% 82% Wrist flexion with fingers flexed (30 s) 66% 95% 91% 78% The manual carpal compression, or Durkan test is performed by applying pressure over the transverse carpal ligament for 30 seconds . Pain or paresthesia indicates a positive result. The average sensitivity and specificity of the manual carpal compression test are 64 and 83 percent, respectively . Recently, carpal compression test has been used to diagnose the CTS. There were many evaluations of sensitivity and specificity of carpal compression test. To make matters worse, the sensitivity and specificity of the carpal compression test depends on physician's examination skill, too 1, 7, 10, 16, 23, 24). Therefore simple to perform .
Objective: The present study evaluated the sensitivity, specificity and predictive values of six clinical tests in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). Methods: There were 29 carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) subjects (mean age 48 years) and 30 control subjects (mean age 45 years). The six clinical tests included Tinel's sign, wrist flexion with fingers extended, wrist .
Phalen's test had a sensitivity of 0.50 and specificity of 0.33. Durkan's test had a sensitivity of 0.71 and specificity of 0.22. Phdurkan test had a sensitivity of 0.84 and specificity of 0.11. Median time to a positive Phdurkan test result was 3 seconds. McNemar tests showed significant differences (P < .05) in the proportions of positive .
Tinel's test is used to test for compression neuropathy, commonly in diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome.[1] Toggle navigation. p Physiopedia; p Physiopedia; About; News; Contribute . Sensitivity Specificity; Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: 25% - 75% 70% - 90% Cubital tunnel syndrome: 70% 98% Diabetic neuropathy: 95% 56% Sensitivity and specificity values were higher for cubital tunnel syndrome and peroneal compression syndrome but lower for carpal tunnel syndrome. Pronator syndrome was also examined, but the data were inadequate for analysis. Carpal Tunnel Physical Exam). A positive test is evident when paresthesias or pain arises within the median nerve distribution during the carpal compression test. This test is associated with a sensitivity of 64% and a specificity of 83%. Even though these tests have a wide range of sensitivity ranging from 57-94% and specificity ranging from 51-97%, still nerve conduction studies (NCSs) are utilized as the gold standard to prove .
Background: The utility of nerve conduction studies (NCS) for diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) has continued to be a subject of debate. Proponents of NCS assume a high sensitivity and specificity; however, many are unaware of the actual literature on this topic and the cutoff values commonly used for diagnosis.
The hand elevation test has higher sensitivity and specificity than Tinel's test, Phalen's test, and carpal compression test. Chi-square statistical analysis confirms the hand elevation test is not ineffective campared with Tinel's test, Phalen's test, and carpal compression test. . Phalen's test had 84.4% sensitivity and 86.7% specificity . Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is the most common compression neuropathy of the upper extremity, happening as the results of median nerve entrapment in the carpal canal [].Persons with CTS have sensory or motor problems in the area innervated by the median nerve [].The prevalence of CTS has been estimated to be 4–5% in the general population, with a .Our purpose was to assess sensitivity (Sn), specificity (Sp), and interrater reliability of the CTS-6 when administered by medical assistants (MAs). . Evaluation of the scratch collapse test for carpal and cubital tunnel syndrome—a prospective, blinded study. J Hand Surg Am. 2020; 45:512-517. Full Text. Full Text (PDF) Scopus (12) PubMed.
Carpal tunnel syndrome, the most common entrapment neuropathy of the upper extremity, is caused by compression . The hand elevation test has similar sensitivity and specificity as the Phalen .
More recently, the carpal compression test was proposed and showed higher diagnostic accuracy over the Tinel sign and Phalen’s test. Almasi-Doghaee et al. (2016) report a sensitivity of 80.6% and specificity of 52.9% which . Buch-Jaeger and Foucher reported that the Durkan/carpal compression test had 49% sensitivity; their review score was 8. In this case the recommendations of a study can be compared with how scientifically it is reported to assist in clinical decision-making. . The sensitivity and specificity of tests for carpal tunnel syndrome vary with the .
The manual carpal compression, or Durkan test is performed by applying pressure over the transverse carpal ligament for 30 seconds . Pain or paresthesia indicates a positive result. The average sensitivity and specificity of the manual carpal compression test are 64 and 83 percent, respectively . The Hoffman-Tinel sign is commonly used to indicate peripheral nerve fiber compression or regeneration.[1] . such as Phalen's or Durkan's tests, which have a greater sensitivity and specificity . Sensitivity and specificity of clinical testing for carpal tunnel syndrome. Can J Plast Surg. 2003 Summer; 11 (2):70-2. [PMC free article . ObjectiveThe present study evaluated the sensitivity, specificity and predictive values of six clinical tests in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome . Median nerve compression test in carpal tunnel syndrome diagnosis. Reproduces signs and symptoms in affected wrist. Orthop Rev 1985; 14: 41–5. Google Scholar. 9.
Phalen’s test; Diagnostic Performance Characteristics. To diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome with high sensitivity and specificity, a positive median nerve compression test needs to be accompanied by a patient completed hand-diagram, the presence of night pain and abnormal sensibility by monofilament testing. A diagnosis of carpal tunnel .
A new test, called the carpal compression test, consists of application of direct pressure on the carpal tunnel and the underlying median nerve. . The sensitivity and specificity of six carpal .
McNemar test was used to compare the follow-up periods. Validity of tests was tested using sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), and accuracy. . Gonzalez I, Lovic A. Value of the carpal compression test in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. J Hand Surg (Br). 1997;22:38–41. Article .
Ma et al. (2012) argue that the hand elevation test is the most accurate physical examination for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome yielding higher sensitivity and specificity than common tests such as the Tinel sign, Phalen’s test, and carpal compression test that you can watch on our channel as well. In their diagnostic study, the test had a . INTRODUCTION. The diagnostic accuracy of clinical screening examinations for carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is controversial. Despite it being the most common compression neuropathy, common clinical tests such as Tinel’s sign, Phalen’s manoeuvre, and Durkan’s test have variable sensitivity and specificity. 1–5 Self-reported questionnaires, such as the 6 .The purposes of this systematic review were to examine the properties of clinical tests usd in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) and to provide estimates of their sensitivity and specificity. A literature search was conducted using two databases—PubMed and the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL)—from 1986 to June 2003, .
The goal of this study is to summarize the current literature on scaphoid fractures to evaluate the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of four different imaging modalities. . The scaphoid is the most commonly fractured carpal bone. . (sensitivity = 85.71% and specificity 29.62%), or a direct compression test (sensitivity = 42.85% and .
provocative testing for carpal tunnel syndrome
Resultado da DraftKings Sportsbook users can wager on the vast majority of teams, sports and events. However, some state betting regulations prohibit wagering on certain sports or athletic events. New Jersey and New Hampshire, for example, do not allow betting on collegiate sports teams from within their .
carpal compression test sensitivity and specificity|cts sensory test accuracy